I’ve always recommended using network cables to extend a (Wi-Fi) home network. I still do.
However, when running new wires is impossible, MoCA, where available, is the second-best alternative. In ideal conditions — fairly easy to achieve — it can deliver a real Gigabit or even 2.5Gbps network connection, equivalent to the entry-level of Multi-Gig. And faster speeds are possible in the future.
You’ll find out in simple terms what MoCA is in this post and tips on building a successful wired network with it. This connection standard is not as straightforward in real life as in principle.
Dong’s note: Since the post on Powerline, I’ve gotten many requests to write about MoCA. This post results from my extensive trial with the MoCA 2.5 standard in multiple homes and offices over a year. I first published it on April 8, 2023, and updated it on May 15 to clarify things further.

MoCA: Simple yet complicated
Short for Multimedia over Coax Alliance, MoCA is another way to build a computer network by leveraging existing infrastructure. It’s similar to Powerline networking, which turns a home’s electrical wiring into network cables.
In MoCA’s case, the existing infrastructure is the coaxial cable, or coax, originally laid to deliver TV signals.
While MoCA can be great, it’s not great enough to install anew. If you remodel your home, it’s best to remove the coax wires and run network cables instead.
You can think of MoCA as the local area network (LAN) side of data-enabled coaxial wiring. On the other side — the wide area network (WAN) — we have Cable Internet (as opposed to Fiber-optic, which requires new wiring completely).
MoCA vs. Powerline
Both standards deliver Ethernet data signals by leveraging existing wiring. MoCA uses coax cables, whereas Powerline uses electrical wires.
Powerline is ubiquitous—it’s available in all homes with electricity. MoCA is only available in those built with Cable TV in mind—new and modern homes no longer use legacy coax cables.
MoCA is reliable and can sustain at true Gigabit or multi-Gigabit, potentially with Full-Duplex.
Powerline is greatly susceptible to interference, wiring, breakers, etc., and always Half-Duplex—it generally can replace only Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) in bandwidth needs.
The MoCA evolution in brief
Like Powerline, MoCA has undergone a few revisions since MoCA 1.0 was first introduced in 2006. MoCA was initially also Half-Duplex, meaning data can travel one way at a time.
However, starting MoCA 2.5, first introduced in 2016 and became widely available a few years later, the standard is rumored to feature Full-Duplex and, with that, becomes a true replacement for network cables.
Half-Duplex is like communicating via walkie-talkies, whereas Full-Duplex is a conversation over the phone.
A MoCA connection generally uses channels to deliver data signals. Each channel functions at a certain frequency, and the higher, the faster the data speed.
The initial standards (MoCA 1.0 and 1.1) use a single channel and caps at 175Mbps — that’s 100Mbps in real-world applications via a Fast Ethernet port. Starting with MoCA 2.0, the standard can bond two or more channels into one for higher bandwidth. MoCA 2.5 can bond up to 5 channels to deliver 2.5Gbps.
It’s important to note that using MoCA 2.5 doesn’t automatically give you the standard’s high speeds — 1.5Gbps, 2Gbps, or 2.5Gbps. That also depends on the network port of the hardware. Specifically, a MoCA 2.5 adapter with a Gigabit LAN port will deliver 1Gbps at most.
Considering the Gigabit or faster speeds, if you start with MoCA today, MoCA 2.5 is the way to go.
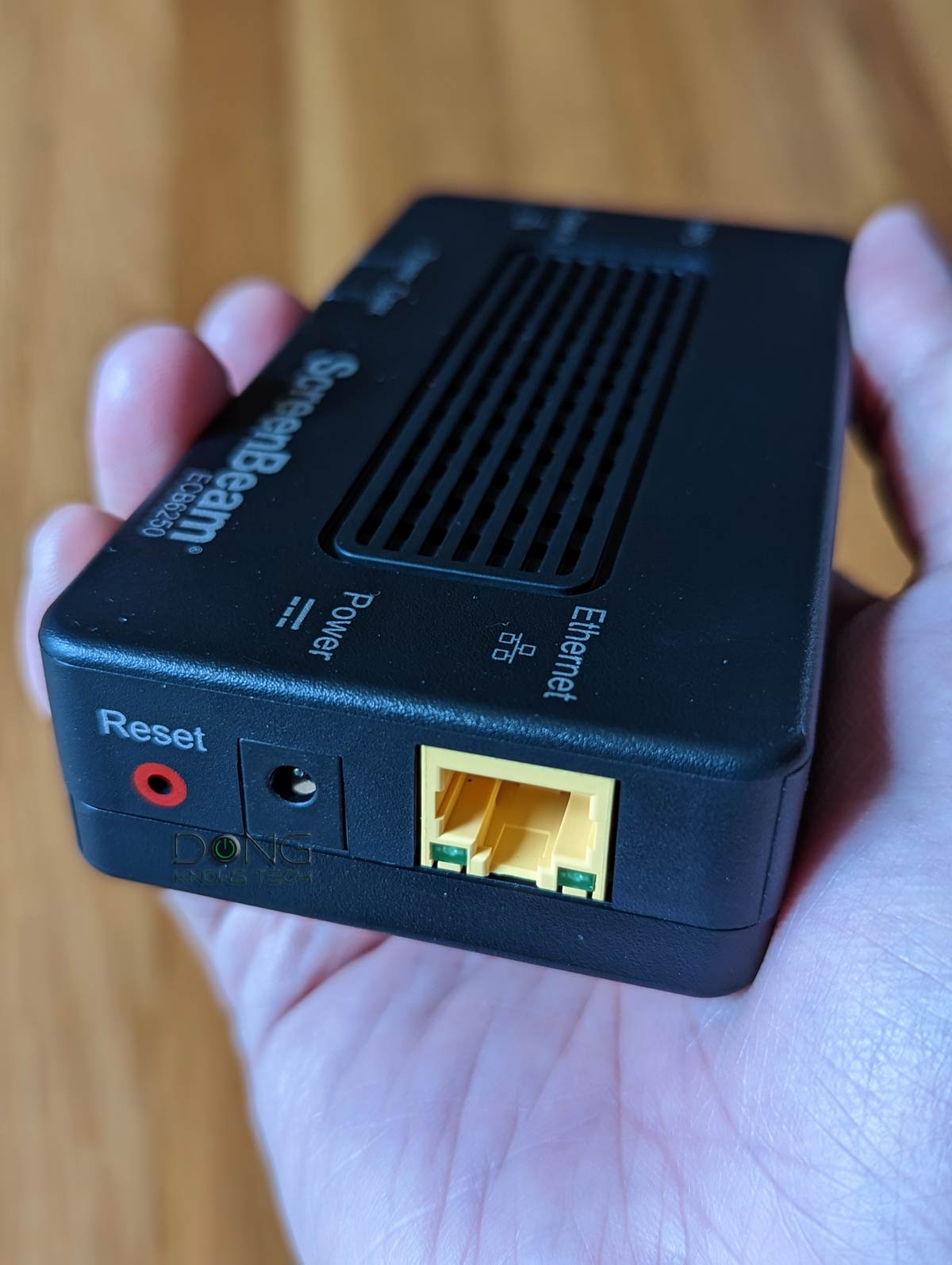
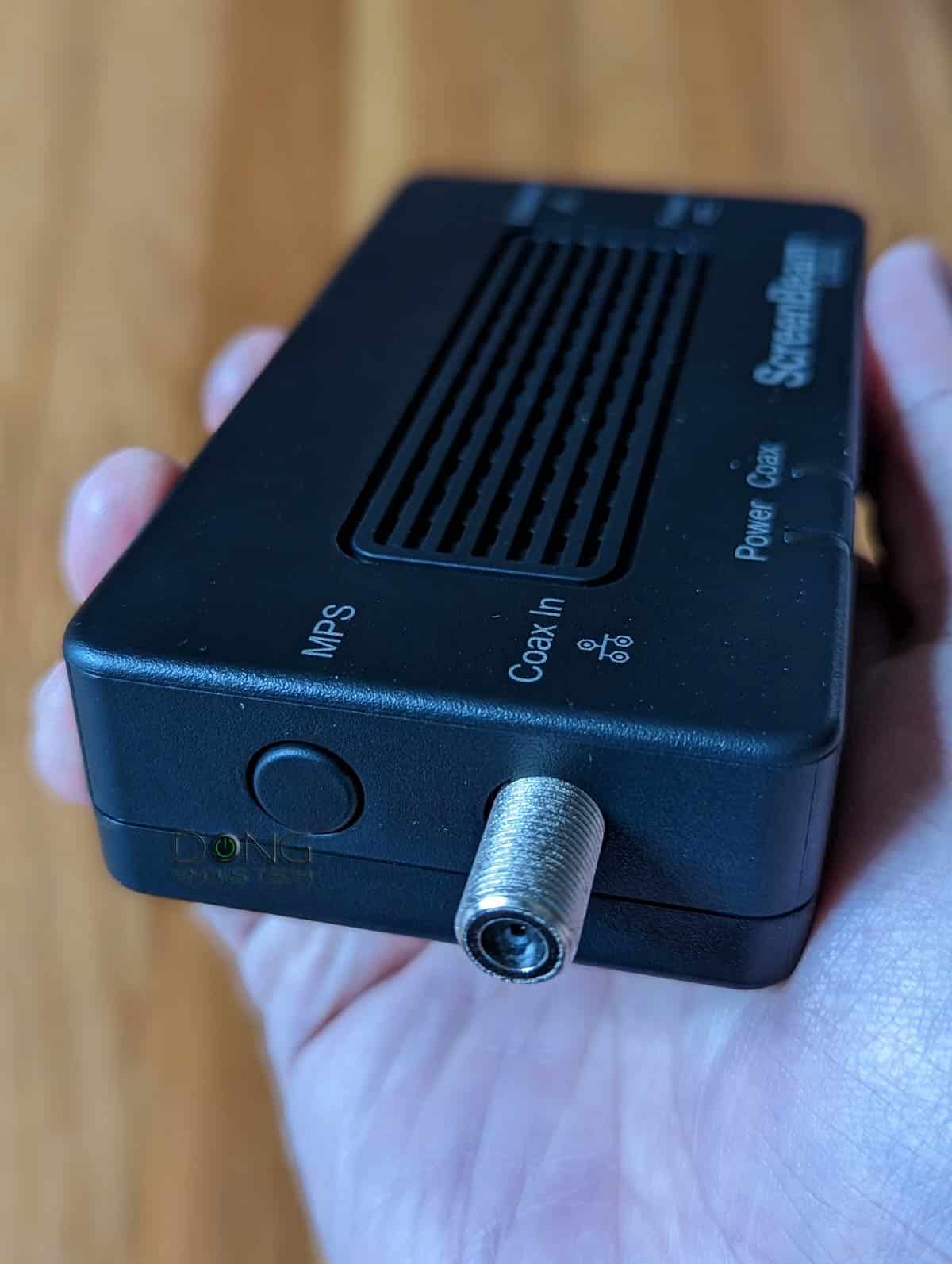


This particular adapter features MoCA 2.5 but comes with a Gigabit port and, therefore, sustains at Gigabit.
MoCA standards
The table below summarizes the existing MoCA standards.
| Version | Number of (bonded) Channels | Max Channel Width | Max Sustained Data Rate | Max Nodes | Half/Full Duplex | Network Port | Advanced Features |
| MoCA 1.0 | 1 | 50MHz | 175Mbps | 8 | Half | Ethernet (100Mbps) | None |
| MoCA 1.1 | 1 | 50MHz | 175Mbps | 16 | Half | Ethernet (100Mbps) | None |
| MoCA 2.0 | 1 or 2 | 100MHz | 500Mbps, or 1Gbps | 16 | Half | Gigabit | Power Saving |
| MoCA 2.1 | 1 or 2 | 100MHz | 500Mbps, or 1Gbps | 16 | Half | Gigabit | Power Saving MoCA Protected Setup (MPS) Management Proxy Enhanced Privacy Network Wid Beacon Power Bridge Detection |
| MoCA 2.5 | 3, 4, or 5 | 100MHz | 1.5Gbps, 2Gbps, or 2.5Gbps | 16 | Half/Full | Gigabit or Multi-Gig (2.5GbE) | Same as MoCA 2.1 |
MoCA 3.0 — capable of 10GbE — is still under development with no estimate of availability yet.
Mixing hardware in MoCA
Generally, newer MoCA standards are backward compatible with the older ones. Additionally, adapters from different vendors are slated to work with one another. In reality, it’s best to use the same adapters throughout.
When you use different adapters, the MoCA connection speed will be that of the slowest one.
If you have to mix adapters, use adapters from the same vendors (different standards) or the same standard (different vendors). In my experience, mixing adapters of different MoCA standards and vendors can be problematic. It might work, or it might not. Your luck will vary.
Speaking of luck, in some situations, using the same adapters can still be hit or miss due to wiring and hardware setup requirements.
How to set up a MoCA network: Principle vs. reality
In principle, MoCA is quite simple and is similar to Powerline.
The objective is to turn the existing coax wiring into network cables by adding MoCA adapters at different coax jacks around the home.
The rule is to get one adapter for each wired device (a.k.a MoCA node) plus one that links all of them to the network — this adapter is often called the main node (or controller node).
The controller node decides the bandwidth of the entire MoCA network — the rest of the nodes will share the controller node’s bandwidth when connecting to the main network or the Internet. However, MoCA supports direct peer-to-peer connections. So, two MoCA nodes can talk to each other without using the bandwidth of the controller node.
There are routers with built-in MoCA, such as the Asus ZenWifi Hybrid XC5. In this case, the main node adapter is no longer needed unless you want to change the standard. (Using hardware with built-in MoCA is convenient, but you lose the flexibility, and compatibility can be an issue when you get a third-party adapter.)

MoCA setup: The simple idea
Here are the standard steps to set up any MoCA network:
- Connect the first MoCA adapter’s network port to your router (or switch) using a network cable and its coax connector to a service jack. This adapter will work as the main node.
- Connect another MoCA adapter to another coax jack and a wired device (such as a desktop computer or a Wi-Fi Access Point).
- Plug the adapters into power.
Repeat the process from step #2 to add up to 14 more nodes.
And that’s it! The adapters will turn the coax cables between them into the network cables to make the wired devices part of the home network. That’s the idea, anyway. And in many cases, that’s all you need to do to make things work.
But sometimes, things don’t work for reasons beyond the obvious such as a wire has been cut or disconnected.
Making sure your coax wires are intact and connected is the first step in building a MoCA-based network — that’s a given.
Let’s look closer.
MoCA setup with diagrams: The Devil in the Details
The coax wiring varies from home to home. In most cases, the Cable drop enters the house at one corner. After that, the Main Splitter immediately splits the line into multiple coax wires that go to different parts of the home and are further divided via more splitters.
TV and broadband signals are lenient with splitters. You can use splitters of any type, almost as many as needed, and cascade them however you want. For MoCA to work (well), things are more restrictive.
The tabs below include two diagrams for typical as-is wiring vs. best-practice (re)wiring that will work for MoCA.
This setup is applicable when you don’t want to do any rewiring. It’s where the chances of success vary greatly.
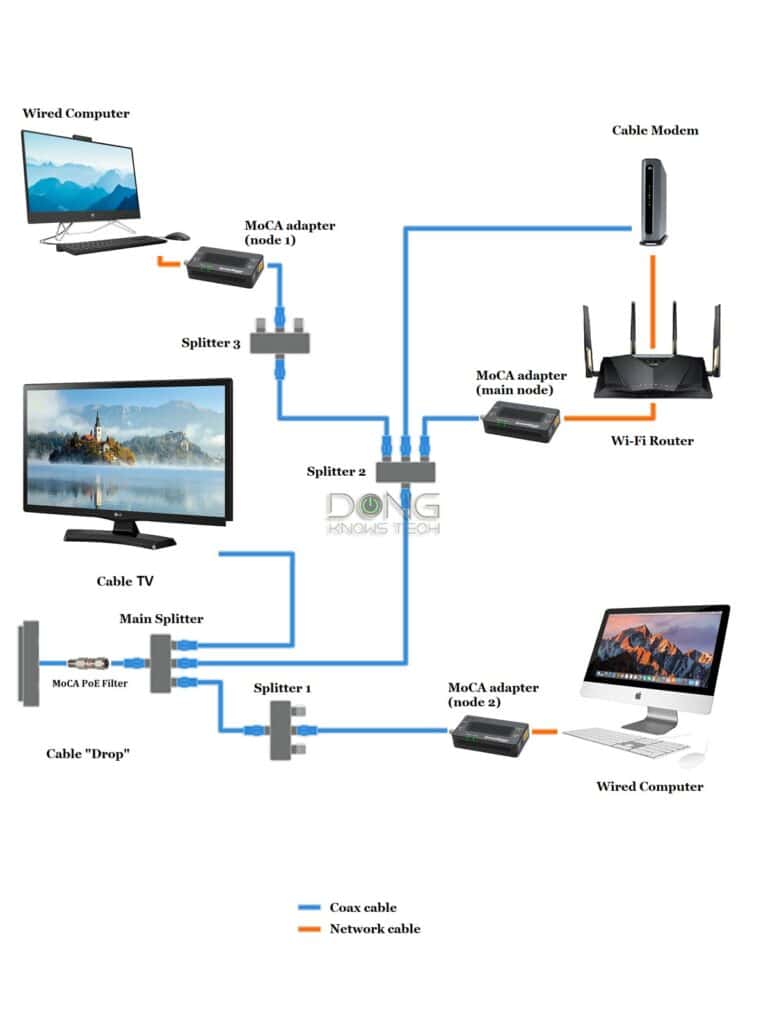
There are two scenarios:
- If you don’t use Cable TV or broadband: Disconnect the service line from the Main Splitter. This is the best scenario since the entire coax network is available for MoCA exclusively.
- If you do use Cable TV or broadband: A MoCA Point-of-Entry (PoE) filter is recommended at the entry point to keep data signals from leaking in or out of the home. (This scenario tends to be hit or miss as-is — check the other tab for more options.)
Additionally, this setup only works if all of the following requirements are met:
- Behind the Main Splitter, there’s no more than one layer of additional splitters. In the diagram above, things will stop working as intended if you add one more MoCA device to Splitter 3. (In practice, this splitter should be removed or replaced by a coax coupler.) To increase the number of MoCA nodes, use large splitters, such as this 8-way splitter, instead of stacking them.
- There is no one-way coax amplifier or amplified splitter within your home. If you use an amplified splitter, replace it. (If you’re unsure, replace all splitters — they are relatively affordable.) Additionally, all splitters should have a frequency range above 1,000 MHz — higher than 1,500MHz is ideal. Technically, a lower-frequency splitter might work, but it often doesn’t.
- You don’t use coax cables for non-Cable TV signals like DirecTV, satellite Internet, DSL, or anything else. MoCA works best as the only application on the coax wiring and can share the same wiring simultaneously only with Cable TV and/or Cable broadband Internet.
- For the best MoCA performance, the maximum cable length between the Main Splitter and the farthest coax jack is 300 feet (90 meters).
This setup applies to those with TV or Cable broadband and is willing to do some rewiring.
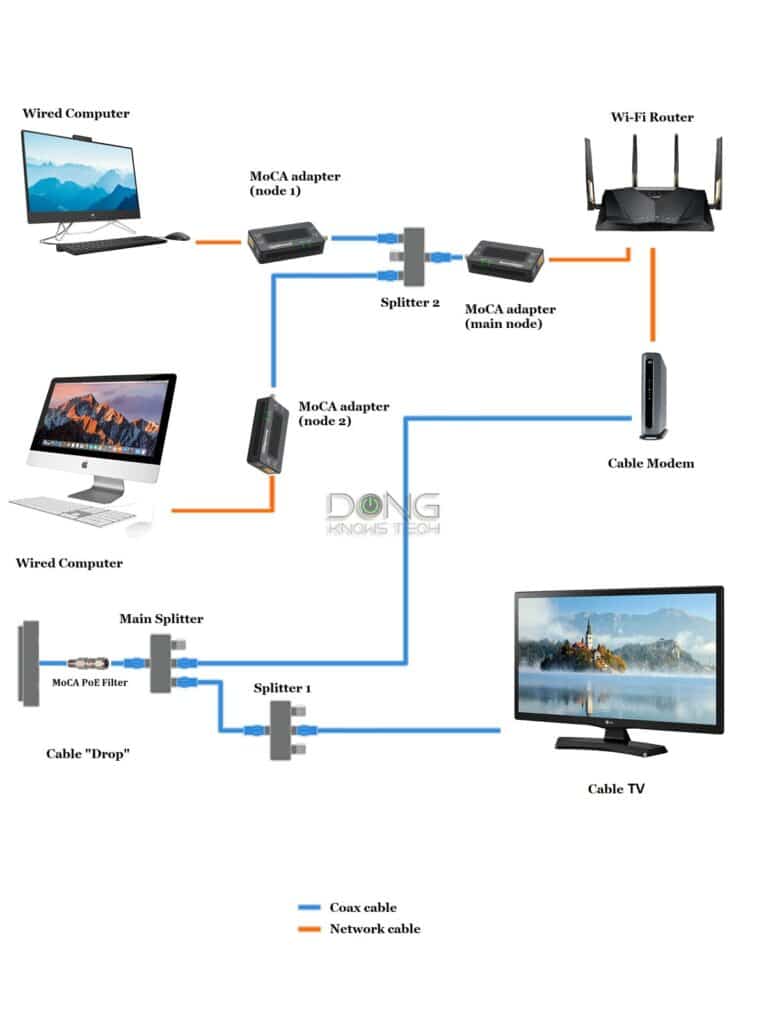
The key to this setup is to separate MoCA from TV or broadband signals. For this setup to work, keep the following in mind:
- The Splitter 2 connected to the Main Node adapter is the only one used for MoCA. To increase the number of MoCA nodes, replace it with a larger splitter, such as this 8-way splitter. You can’t add another one on top.
- This splitter should be MoCA-ready. Specifically, it should have a frequency range above 1,000 MHz — higher than 1,500MHz is ideal.
- For the best MoCA performance, the maximum cable length between MoCa adapters is 300 feet (90 meters).
And that’s it. Your MoCA network should now work.
Tip
Undecided between two different adapters of the same specs? Get the less expensive one. Besides the hardware specs, MoCA adapters are generally very similar in functionality.

MoCA: The takeaway
MoCA, where available, can be an excellent alternative to network cables. But it may have a learning curve.
Here are a few recap bullet points to better the chance of success:
- Always get adapters from the same vendor and of the same standard (MoCA 2.5 or later is recommended). Also, mind the Ethernet port. A MoCA 2.5 adapter only delivers top speeds if it has a 2.5GbE network port — many have a Gigabit port, but that is enough in most cases.
- Use splitters with a large frequency range designed for MoCA.
- To host more devices, use large splitters instead of stacking smaller ones over two layers within the home.
- It’s best to use MoCA for the network signals alone by:
- If you don’t use TV or Cable broadband service: Disconnect the service line at the entry point.
- If you have TV or Cable broadband service:
- Separate the wiring and use MoCA independently (best). or
- Install a MoCA PoE Filter at the entry point (not ideal).
The easiest and best way to use MoCA successfully is to find the two ends (two jacks) of an intact coax wire for the two adapters(*). Often, that single MoCA link is all you’d need to have a mesh system with a reliable wired backhaul or be able to place your standalone router at the ideal location within the home.
Tip
(*) Replacing the splitter that hosts two separate coax cables with a coupler will turn them into a single line ideal for MoCA — it’s separate from the rest of the coax network used for the original purposes, such as TV or broadband.
If you live in a home with extensive coax wiring and want to build a MoCA-based home network, picking the correct coax splitters and stacking them correctly is the key — that’s especially true if you don’t want to do any rewiring. Still, since it’s hard to trace the wires behind the walls, your chance of success will vary.
Finally, nuance is the key. Just because the standard can handle up to 16 nodes doesn’t mean you want to use them all. It’s best to keep the number of nodes below five and use network cables when possible.






Hey Dong,
You are a reputable source and thought I pose my question to you.
My house has CAT 4, changing that is a expensive option, hence I decided to go the MOCA router. I have a 2 GB Gfiber and use their 6e router (GR6EXX0).
My set up consists of 4 moca nodes all are Screen Beam ECB 7250 with of them is the primary/master node is connected to my routers 2.5 GB port. I checked the output to confirm I am getting a ~2GB down and ~1GB Up. I plug the master to the existing coaxial outlet. after this is a blackbox, and on the other end I connected a another 7250, but get only 1.2GB. I am understand there is going to be some signal lose, but didnt expect 40% loss.
I have a finished basement and have small panel with bunch of coaxial cable connected to some splitter. I disconnected a few that I know i am not using, but didn’t help much.
I am looking for your advice on how I can reduce the signal loss and increase the speed to get close to 2GB.
1. Will adding a coaxial signal booster help?
2. Terminating unused terminals, help?
This happens a lot, Sam. Like others, you didn’t pay attention and made wishful assumptions based on the vendors marketing ploy. The speed of the adapter is limited by its network port. Give the post a careful read.
Dong,
Thanks! for the quick response. the ECB7250’s theoretical throughput for the LAN port is upto 2.5Gbps. What am I missing?
additionally, I ordered a 2 MOCA PoE filter you recommended. lets see how this works
No it is NOT, Santhosh. That’s the point. You missed this part. Read every single word of it from top to bottom.
Update.
I am finally getting the full 2 Gbps down and ~1 Gbps up with the MoCA 2.5 adapter. Here is what i did
1. Terminate all open coaxial port around the house.
2. Disconnected the connection from the external source.
3. Added the PoE MoCA filter you mentioned above.
In the home wiring diagrams it is clearly implied you have at least one room with two coax taps running into it, one indirectly attached to a router through a cable modem and another indirectly attached to the same router through a MoCA adapter. I have never seen a house with more than one coax tap per room as original equipment. Even in a large area like a living room there’s usually only one tap in some inconvenient location the house designer thought a TV should go. If there is another tap it’s very far away, perhaps on an opposite wall, forcing a run of tens of feet of ugly and hard to hide ethernet to bridge them. So where exactly is the router supposed to go?
You just need a short coax cable for the modem or router, Bob. Not all devices need a wall outlet (which what I think you meant by “tap”?), a simple splitter and two short, as short as less than a foot, cables will do. Have a bit of imagination and pay some attention, you’ll figure things out.
Which of them doesn’t need a wall outlet? In the “best practice” diagram they clearly go to different splitters. Unfortunately the diagram doesn’t show where the wall outlets are, if they are different than the coax runs.
Are you saying that the cable modem and the MoCA adapter that run to the router on their ethernet side are running to the same wall outlet on their coax side, with an additional splitter not in the diagram joining their coax runs to the wall?
An outlet is just a terminal of a cable, Bob. You can take it out of the picture. Or not. But I can’t imagine for you. Good luck!
MoCA related. I have been using MoCA adapters and have found them to work well. I recently switched from cable internet to Fiber. The previous 3-way splitter being used for the coaxial cables had an IN port and 3 OUT ports connected. With Fiber there is nothing going to the IN port. I realize I can just cap this port, but was wondering if the splitters are bidirectional could I use a 2-way splitter instead and just connect one of the coaxial cables to the IN port?
Use a different splitter, Ron. But it’s best not to use one. Read the post carefully.
Hi, this is a great article but I wanted to offer a friendly correction – MoCA 2.5 is still simplex (a.k.a. “half duplex”) communication, just like all the versions of MoCA that came before it. We won’t have duplex MoCA until version 3.0, which should bump the link speeds to 10 Gbps (~8.5 Gbps actually usable) in both directions simultaneously under perfect conditions. Hopefully we’ll start to see the new generation of gear in the next year or two.
I haven’t been able to get a concrete answer on this, but thanks for the input, Tate.
Sure thing! For what it’s worth, I have a set of four MoCA 2.5 adapters in my lab that I used to confirm that MoCA 2.5 and G.hn Wave 2 could coexist on the same coax segment for work (ISP network engineer) a while ago. I tested throughput using 2.5GBASE-T equipped clients sending multiple TCP iperf3 streams to each other over the MoCA network. With only one client sending and everyone else quiet, I observed ~2.3 Gbps of lossless throughput. But with two clients sending to each other simultaneously, the observed throughput of both was essentially halved. I’d be happy to replicate the testing and share more detail about the setup if you or any of your readers might find it helpful.
Thanks for the offer, Tate, but I don’t want to dive into MoCA any further. It’s just a supplement to my “get your home wired” approach.
Great article! I just bought three MoCA 2.5 adapters to establish an Ethernet backhaul for my WiFi mesh and your article clarified a number of points.
I might still start with a typical setup but am definitely considering the best practice one.
One question regarding splitters: as far as I understand, MoCA 2.5 adapters operate within the frequency range of 1125 MHz to 1675 MHz so shouldn’t splitters cover at least that range? Typical splitters found at local DIY store are only rated to 1000 MHz…
That was mentioned in the post, just in different wording.
Great article and most complete set of recommendations I have seen and I have spent way too much time looking at Moca stuff.
?
Can a single Moca adapter be used to convert broadband over coax that is already split at incoming service (Cox) service going to separate buildings where there is already a modem?
Guess am asking if Moca adpater serves same function as cable modem in pulling Internet off the coax and converting to Ethernet?
Have friend that has both restaurant biz and cabins on Cox biz service and a separate/split line buried to house about 60-70 meters away that has broadband on that line. Took the cable modem at biz office to house with router and confirmed that wire has Internet signal on it.
Or will we still need 2 Moca adapters, splitter, filter …?
Thanks in advance and glad I found your site.
Will be purchasing the ScreenBeam and other items listed from Amazon.
No. The gist of it is that before being converted into a networks cable, a coax cable can’t work as a network cable, and once converted (by two adapters at both ends) it can work however a network cable is used. Any assumption outside of that has nothing to do with MoCA and will unlikely work.
Figured but thought it was worth asking.
Thanks!
👍
Hi Dong,
I have a PoE filter at the point of entry of the COAX cable entering the house. Do you think its necessary to have another PoE filter before the cable modem to limit interference with teh DOCSIS 3.1 modem? Or is this not necessary?
Also, I have a coax splitter but the range is 5-2450mhz, would i have any issues with MoCA 2.5 using this high of range? I can still return it if 5-1675mhz splitter is more ideal.
If the splitter is in the frequency range then it should work fine. There is no need for wo PoE filters. In fact my cause issues in some cases.
As mentioned, anything 1000MHz and higher works, Jackie. And no, you don’t need a second filter.
I’m attempting to choose between Moca 2.0 and Moca 2.5, and the lower-latency full duplex ability of 2.5 appeals. However, I can’t find anywhere else stating it’s full duplex, even mocalliance.org. Can you provide a source where you found 2.5 to be full-duplex?
Thanks
I got the info from a vendor and the connection was indeed fast during testing so I took their word for it. If you’re so adamant about this, it’s best to run network cables. I don’t use MoCA for myself.
I’d love to, and have fished many a cable through walls, but sometimes construction makes it really difficult (to be brief).
Which vendor was it? Screenbeam or goCoax?
Thank you
I don’t remember, Don. It’s been a while since that conversation. Sorry, I can’t be of any more help on this quest. You can take my word for it or not. In your case, it doesn’t hurt to go with the latest standard.
I am hostile to coax cable, simply because it is stiff and difficult to work with. Cat5e and Cat6 cables allow transmission as fast as I can afford to pay for. Yes, my ISP uses coax cable, so a cable modem is needed but everything beyond it uses twisted pair or wireless. That, of course includes connection from the cable modem to the router. For TV I use streaming. My ISP occasionally interferes delivery of a video news service it owns
. But my wife and I also subscribe to four news services, including two of the three national “newspapers,” one regional service and one Michigan and local area-oriented service. And, of course, Dong’s site.
Dong, do you have any specific brand of adaptor that you prefer over the others? Also, I read in an AMZN review that some adaptors have a web GUI to test speed/ performance in real time. Not sure how that is even possible. Can you eleborate?
Thanks again!
I know you didn’t ask me but I just did my research and set my network up last week and I had good luck (and read great reviews, best price for two, etc.) with these: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B08MQGT61
You can use the ones I mentioned in the post. I’ve used them both.
Can you use a MOCA adaptor between the optical modem and the router? Optical modem – MOCA – coaxial cable – MOCA – Router.
Yes, Ivan. MoCA adapters turn the coax wire into a network cable and all that implies.
Great article. {…}
Secondly, I can’t add my filter to the demarcation point (in the ISP’s box outside). So I put it on the outlet that’s coming into my condo/home. Do you recommend putting it somewhere else? I’m security-minded with many neighbors, so I want anything traffic leaking in or out.
I recommend you follow the rules above before asking any questions. No spamming, please.
My house is currently wired with coax, but we don’t have active cable TV. It’s all streaming for us. Due to this, would we still need filters in place?
Also, we have a few concentrations of devices at remote corners of our house. I don’t see any reason why not, but just want to check. There should be no issue with using a small 4 or 8 port GigE switch just before a MoCA adapter to wire in our TV/AppleTV/PS4/etc, right?
Thanks for all your valuable info!
Give this post a *good* read, David. You might want to do that on a desktop browser (and not a phone) to see things clearly.
Nope! You won’t need filters, the filters are for cable TV (=
No issues with small switch at the end of the corners of the house too. You’re good to go!
Thanks, I thought so but was just looking for confirmation.
Hi Dong,
Is it possible to connect mesh routers via both ethernet cables and a MOCA adapter? The setup is as follows:
Verizon FIOS (both TV and internet). I ran an ethernet cable from FIOS router to my own ASUS Zen Wifi router (both in basement) and use the ASUS as my main router(double NAT situation). I then ran an ethernet cable from the main ASUS router to a satellite router on my first floor. The issue I am having is the coverage on the second floor is spotty (I also have a satellite router on the second floor which has a wireless backhaul at the moment). It is not really feasible for me to run an ethernet wire from the first to second floor, however coax wiring is already installed throughout the house including the second floor. Is it possible to use a MOCA adapter to connect the satellite router on the second floor? Or would it not work mixing ethernet and MOCA as backhaul?
MoCA, when used, is actually a network cable Chris. In other words, add two MoCA adapters to the two ends of a coax cable and that cable is now a network cable. You can’t “mix” the two since they are one.
For your case, the single connection I mentioned at end of the post applies. Good luck!
Thanks for the reply. I tried to give it a go, but in all likelihood I’m running in the splitter issue you mentioned in your article as nothing worked after I connected both MOCA adapters. Oh well, maybe one day if I remodel my house, I’ll be able to run an ethernet cable from floor 1 to 2.
👍
Hi Dong,
New Verizon Fios user. I was given free MoCA Adapter a month later (promo) for getting 1 Gig internet. Went from 200 mbs to 1 Gig for less money. Went down Double NAT trail on purpose (re read your posts beforehand and was ok with the projected slowdowns) to isolate my RING, IoT stuff etc. I’m using Asus AX86U and Asus AX88U for my inside NAT. Pre MoCA I had 900 and 900 (variable) up and down, on the double NAT. For my use, that’s great! Installed MoCA when it arrived to re arrange and utilize the Verizon WiFi Node and increase my Ring WiFi coverage etc…..and speeds crashed….like really crashed to 30 up and 2 down. Checked all settings, rebooted, reset etc. Mediocre results. I removed the Moca and went back to previous locations of Verizon 3200 Nodes (main router is CRA1000A). Now fluctuates between 500 to 900 down and 50 to 150 up. I know its rude to ask for free advice, but my question is my MoCA was 2.5, the splitters given by Verizon were 2.0 ghz. Are the splitters gonna make that much of a difference? Would that affect the Up and Down speeds behind the 2nd NAT? Been thinking about a Firewalla Gold to restructure and fix the Double NAT, but not sure if Verizon Fios will play nice.
Thanks for your time
It looks like MoCA is not necessary in your case, Stephen, and when you used the adapters, they seamed to function at Fast Ethernet for one reason or another. It’s impossible for me to have the correct assessment of your situation.
Hi Dong, thank you for writing this article! I’ve been reviewing this and other sites/forums to try to understand MoCA in preparation for my own set up. One thing I’ve seen recommended in several scenarios is a second PoE filter located at the modem. In which cases is that second filter needed?
I’m currently using a Coda 4582 bridged to an ASUS ET8 in router mode, and I’ll be using MoCA to establish a wired backhaul to the second ET8 unit (the wireless backhaul is not very useful, as you’ve alluded to in your ET8 article). I have a PoE filter at the service line entrance to the home, but I’m wondering if I would need a second one at the 4582, and also want to understand what the purpose of that second filter is.
No, you won’t need a second filter at the modem, Wade. It won’t do anything. The filter is to keep outside MoCA signals (such as those of your neighbors) from entering your home. In most cases, no filter is needed. It’s a recommended device, just in case.
I had originally tried MOCA 2.5 in my house but discovered that my coax cable isn’t very good. I can’t even handle a single split from where the cable comes into the house; it causes too much signal degradation at the cable modem even when using the correct types of splitters. So had to settle for wireless backhaul on Asus ET12 which has worked pretty good. Someday I’ll run network cable if I ever need it though.
You might just replace that splitter with a better one, James. I’ve run into this a lot. But no, nothing beats real network cables.
Even a splitter with a high enough frequency (1675 MHz and beyond) may degrade cable modem signals and thus speed (which is fed back thru the router to the MoCA adapter).
Have you tried a cable tap like the one at https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0UVW2VU4
instead of a splitter? I bought mine for less than $10 including tax & shipping.
It just has .5 dB loss at the “pass thru” to the cable modem (should barely notice a difference) and the “tap” (out to the MoCA adapter) loses 10 dB, but most say they still get great MoCA signal/speed. The important thing is not to degrade your cable modem signal from the get go.
Thanks for the tip! Unfortunately I sold my MOCA adapters so I can’t try it. My all-wireless ET12 setup has been working great so I haven’t needed the MOCA anyway. If I ever do want a wired setup I’d probably just run outdoor-rated ethernet cable from one side of the house to the other anyway.
👍
Very good article. I have recommended MoCA to friends and set some up devices in my family member’s homes. I also remind people to make sure they have a POE filter to make sure the MoCA signal doesn’t escape their home (usually installed at the point of demarcation). Often I hear people complain their MoCA device is having issues. People don’t realize all the splitters need to be MoCA rated and the coaxial lines in the wall rated RG6 vs RG59 usually perform better with MoCA. I have reached speeds on my laptop over 1400 mbps down using MoCA devices. Great alternative to ethernet.
Thanks for the input, TDobb! I added the info in your honor. It was overlooked originally.
Thanks for the well written and informative article! I knew some MoCA stuff, but the advice on frequency recommendations and splitter advice are things I had not considered.
Question – I see affiliate links for splitters, but I’m surprised no links to recommended or reviewed MoCA adapters? Not even the ones in the article? Perhaps I’m misinterpreting the “extended trial” part of the article to mean that a review article or recommendations of MoCA 2.5 adapters is still in progress?
I see no question in your comment, Gordon, just assumptions. I don’t think you know what I do with my time, or are entitled to have any say about it, so take or leave it?
As for affiliate links, that’s the default on this site.
I’m gonna use this for my mesh backhaul – I don’t have ZenWiFi hybrid XC5 and am only thinking in a couple or so when I move into WiFi 7. am not in any rush, might bide my time to see if any moca 3 hardware hits the market by then 🙂
Good call, David! It’ll work well if you keep the splitters in check. They are relatively inexpensive, and some MoCA adapters include them.